Vue3 核心特性与实践指南
Vue3 是一个革命性的版本,它不仅带来了性能的提升,更重要的是引入了组合式 API,彻底改变了我们编写 Vue 组件的方式。本文将深入探讨 Vue3 的核心特性,并通过实际案例展示如何更好地使用这些特性。
1. 组合式 API (Composition API)
组合式 API 是 Vue3 最重要的特性之一,它解决了 Vue2 中代码组织的问题,使得逻辑复用和代码组织变得更加灵活。
1.1 基础概念
setup()是组合式 API 的入口点,它在组件实例创建之前执行- 由于
setup在组件实例创建之前执行,所以无法访问this - Vue2 的选项式 API 写法仍然完全兼容,可以渐进式迁移
setup函数接收两个参数:props和context
import { defineComponent } from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
props: {
title: String
},
setup(props, context) {
// props 是响应式的,但不要解构它
console.log(props.title)
// context 包含 attrs, slots, emit 等
const { attrs, slots, emit } = context
return {
// 返回的内容会暴露给模板
}
}
})
1.2 响应式系统
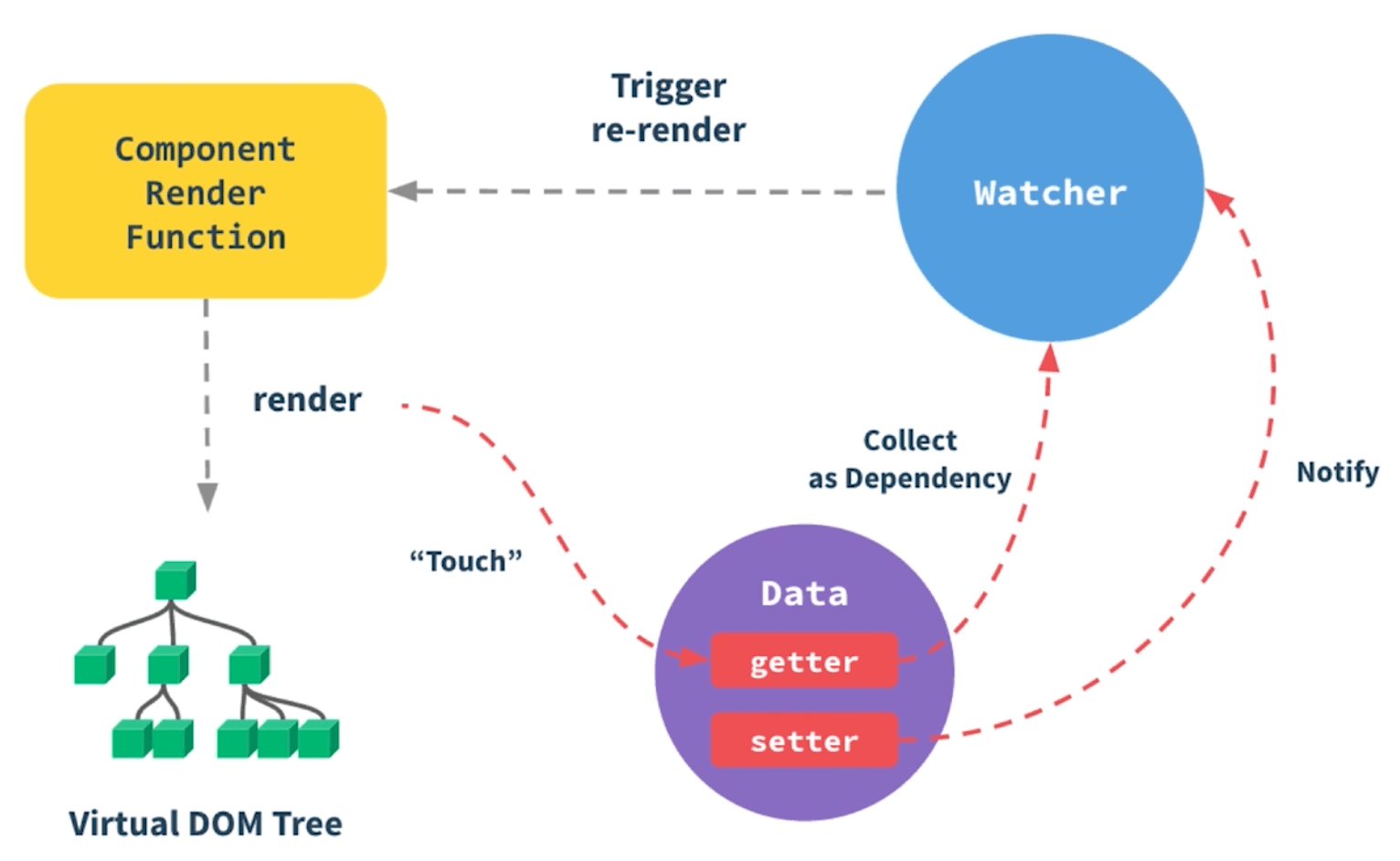
Vue3 的响应式系统基于 Proxy 实现,提供了更强大的响应式能力。
ref 的使用
import { ref, watchEffect } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
// ref 用于基本类型的响应式
const count = ref(0)
// 访问 ref 的值需要使用 .value
console.log(count.value) // 0
// 在模板中会自动解包,不需要 .value
const increment = () => {
count.value++
}
// watchEffect 会自动追踪依赖
watchEffect(() => {
console.log('count is:', count.value)
})
return {
count,
increment
}
}
}
reactive 的使用
import { reactive, computed, watch } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
// reactive 用于对象的响应式
const state = reactive({
count: 0,
double: computed(() => state.count * 2),
history: []
})
// 监听单个属性
watch(
() => state.count,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
state.history.push({
newValue,
oldValue,
timestamp: new Date()
})
}
)
// 深度监听对象
watch(
() => state,
(newValue) => {
console.log('state changed:', newValue)
},
{ deep: true }
)
return {
state
}
}
}
1.3 生命周期钩子
Vue3 的生命周期钩子都带有 on 前缀,并且只能在 setup 中使用:
import {
onBeforeMount,
onMounted,
onBeforeUpdate,
onUpdated,
onBeforeUnmount,
onUnmounted,
onErrorCaptured
} from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
onBeforeMount(() => {
console.log('组件挂载前')
})
onMounted(() => {
console.log('组件已挂载')
// 可以在这里进行 DOM 操作
})
onBeforeUpdate(() => {
console.log('组件更新前')
})
onUpdated(() => {
console.log('组件已更新')
})
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
console.log('组件卸载前')
})
onUnmounted(() => {
console.log('组件已卸载')
// 可以在这里清理定时器、事件监听等
})
onErrorCaptured((err, instance, info) => {
console.error('捕获到错误:', err)
return false // 阻止错误继续传播
})
}
}
2. 响应式工具函数
2.1 toRefs 和 toRef
import { reactive, toRefs, toRef } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({
count: 0,
name: 'Vue3'
})
// toRefs 将整个对象转换为响应式引用
const { count, name } = toRefs(state)
// toRef 创建单个属性的响应式引用
const countRef = toRef(state, 'count')
// 这些引用都是响应式的
console.log(count.value) // 0
console.log(name.value) // 'Vue3'
return {
count,
name,
countRef
}
}
}
2.2 其他响应式工具
import {
isRef,
unref,
isReactive,
isReadonly,
markRaw
} from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
const count = ref(0)
// 检查是否是 ref
console.log(isRef(count)) // true
// 获取 ref 的值,如果不是 ref 则返回原值
console.log(unref(count)) // 0
const state = reactive({})
// 检查是否是响应式对象
console.log(isReactive(state)) // true
// 检查是否是只读对象
console.log(isReadonly(readonly(state))) // true
// 标记对象为非响应式
const raw = markRaw({ count: 0 })
}
}
3. 自定义 Hook
自定义 Hook 是组合式 API 最强大的特性之一,它让我们能够轻松地复用逻辑。
3.1 鼠标位置 Hook
import { toRefs, reactive, onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue'
function useMousePosition() {
const state = reactive({
x: 0,
y: 0,
isMoving: false
})
const updateMouse = (e: MouseEvent) => {
state.x = e.pageX
state.y = e.pageY
state.isMoving = true
// 使用 requestAnimationFrame 优化性能
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
state.isMoving = false
})
}
onMounted(() => {
document.addEventListener('mousemove', updateMouse)
})
onUnmounted(() => {
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', updateMouse)
})
return toRefs(state)
}
3.2 网络请求 Hook
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
interface UseFetchOptions {
immediate?: boolean
onSuccess?: (data: any) => void
onError?: (error: Error) => void
}
function useFetch<T>(url: string, options: UseFetchOptions = {}) {
const data = ref<T | null>(null)
const error = ref<Error | null>(null)
const loading = ref(false)
const fetchData = async () => {
loading.value = true
try {
const response = await fetch(url)
data.value = await response.json()
options.onSuccess?.(data.value)
} catch (e) {
error.value = e as Error
options.onError?.(e as Error)
} finally {
loading.value = false
}
}
if (options.immediate) {
onMounted(fetchData)
}
return {
data,
error,
loading,
fetchData
}
}
// 使用示例
export default {
setup() {
const { data, error, loading, fetchData } = useFetch('/api/users', {
immediate: true,
onSuccess: (data) => {
console.log('数据加载成功:', data)
}
})
return {
data,
error,
loading,
fetchData
}
}
}
4. Teleport 组件
Teleport 是 Vue3 新增的组件,用于将组件的内容传送到 DOM 树的其他位置。这在处理模态框、弹出框等场景特别有用。
<template>
<div class="app">
<button @click="showModal = true">打开模态框</button>
<Teleport to="body">
<div v-if="showModal" class="modal-overlay" @click="closeModal">
<div class="modal-content" @click.stop>
<h2>{{ title }}</h2>
<p>{{ content }}</p>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button @click="confirm">确认</button>
<button @click="closeModal">取消</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</Teleport>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
export default {
props: {
title: {
type: String,
default: '提示'
},
content: {
type: String,
required: true
}
},
setup(props, { emit }) {
const showModal = ref(false)
const closeModal = () => {
showModal.value = false
emit('close')
}
const confirm = () => {
emit('confirm')
closeModal()
}
return {
showModal,
closeModal,
confirm
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.modal-overlay {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.modal-content {
background: white;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 8px;
min-width: 300px;
}
.modal-footer {
margin-top: 20px;
text-align: right;
}
.modal-footer button {
margin-left: 10px;
}
</style>
5. 性能优化
Vue3 在性能方面有显著提升
5.1 虚拟 DOM 优化
- 静态树提升:将静态内容提升到渲染函数之外
- 静态属性提升:将静态属性提升到渲染函数之外
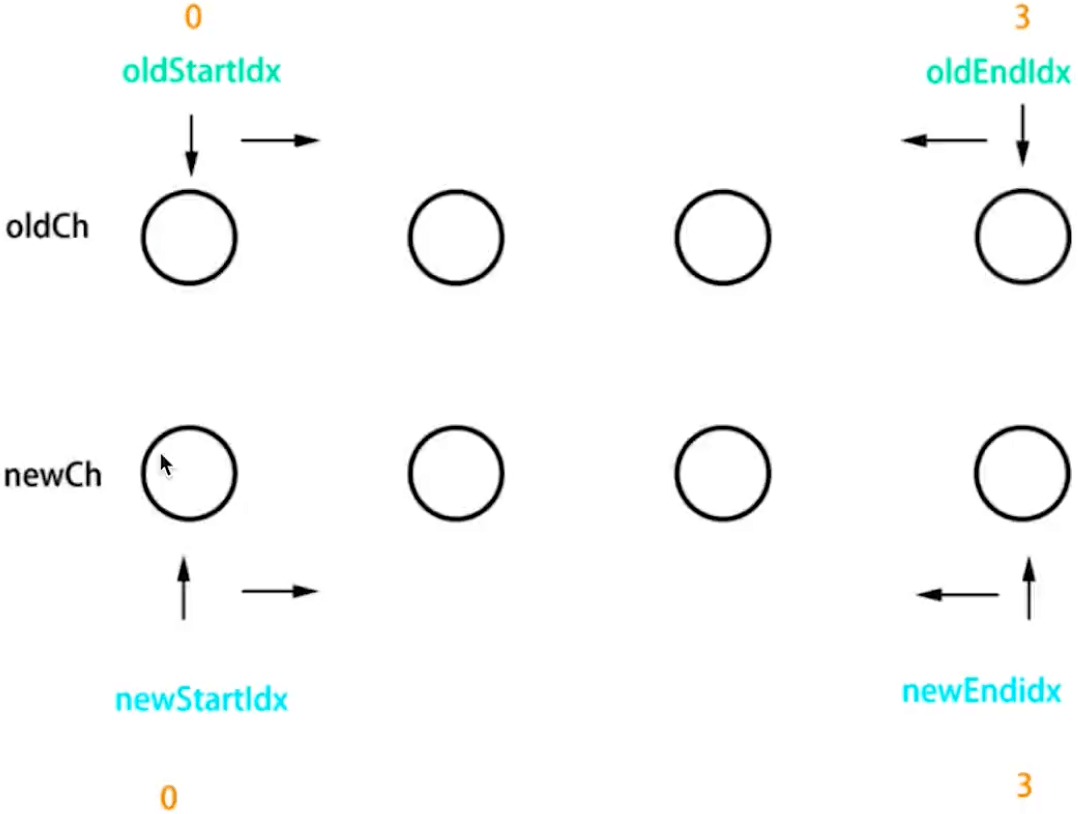
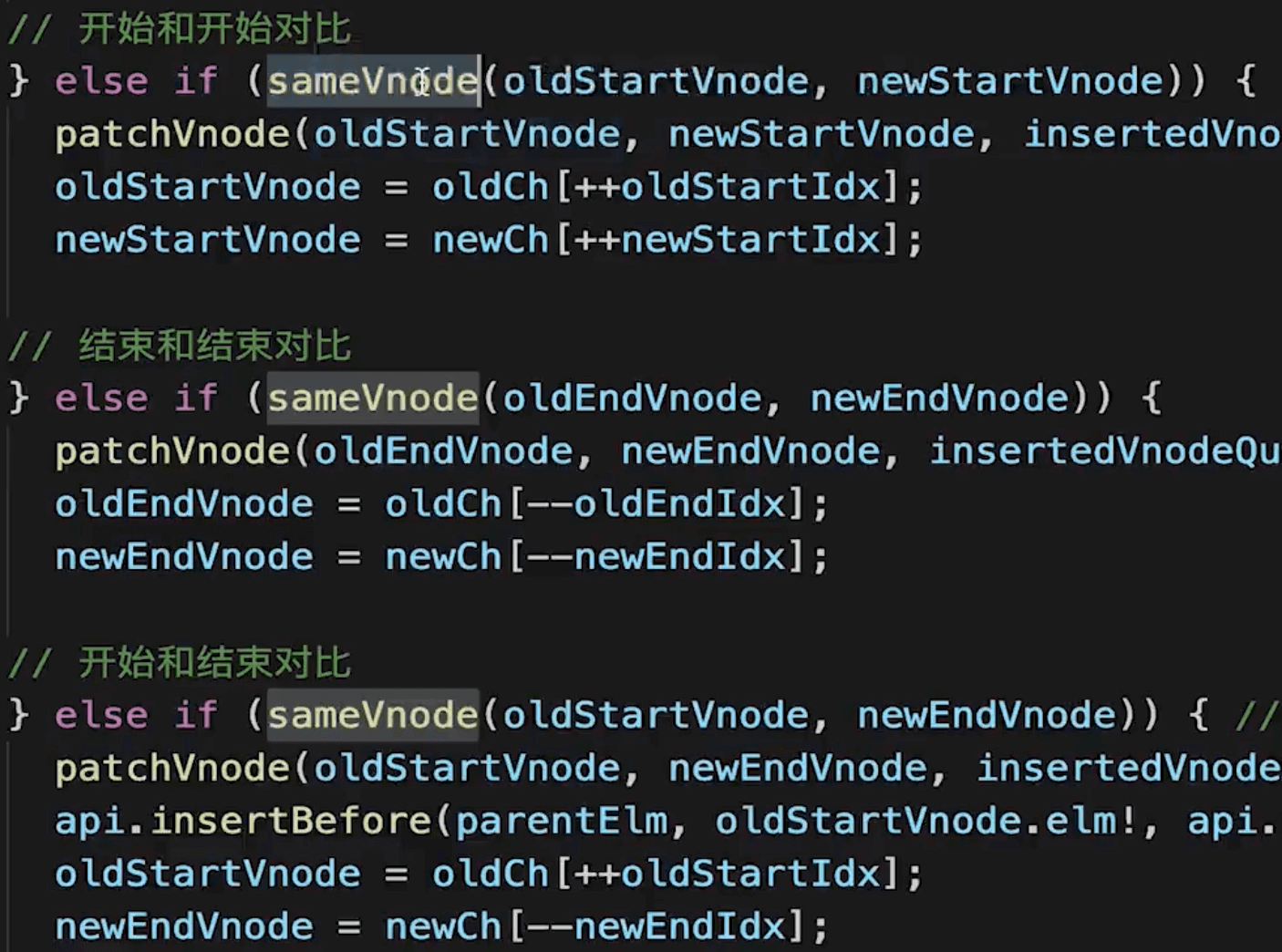
- 补丁标记:为动态节点添加标记,优化 diff 算法
5.2 响应式系统优化
import { shallowRef, shallowReactive, markRaw } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
// 浅层响应式,只跟踪顶层属性
const shallowState = shallowReactive({
user: {
name: 'Vue3',
address: {
city: 'Beijing'
}
}
})
// 浅层 ref,只跟踪 .value 的变化
const shallowRef = shallowRef({
count: 0
})
// 标记为非响应式
const staticData = markRaw({
config: {
theme: 'dark'
}
})
}
}
5.3 组件优化
import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue'
export default {
components: {
// 异步组件
AsyncComponent: defineAsyncComponent(() =>
import('./AsyncComponent.vue')
),
// 带加载状态的异步组件
AsyncComponentWithLoading: defineAsyncComponent({
loader: () => import('./AsyncComponent.vue'),
loadingComponent: LoadingComponent,
errorComponent: ErrorComponent,
delay: 200,
timeout: 3000
})
}
}
6. TypeScript 支持
Vue3 使用 TypeScript 重写,提供了更好的类型支持。
6.1 组件类型定义
import { defineComponent, PropType } from 'vue'
interface User {
id: number
name: string
age: number
}
export default defineComponent({
props: {
// 基础类型
title: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// 对象类型
user: {
type: Object as PropType<User>,
required: true
},
// 数组类型
items: {
type: Array as PropType<User[]>,
default: () => []
}
},
setup(props) {
// props 类型会被正确推导
console.log(props.user.name)
return {}
}
})
6.2 组合式 API 类型
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
interface State {
count: number
name: string
}
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
// ref 类型
const count = ref<number>(0)
// reactive 类型
const state = reactive<State>({
count: 0,
name: 'Vue3'
})
// computed 类型
const double = computed<number>(() => count.value * 2)
return {
count,
state,
double
}
}
})
7. 调试技巧
7.1 渲染追踪
import { onRenderTracked, onRenderTriggered } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
onRenderTracked((event) => {
console.log('组件渲染追踪:', {
target: event.target,
type: event.type,
key: event.key
})
})
onRenderTriggered((event) => {
console.log('组件渲染触发:', {
target: event.target,
type: event.type,
key: event.key,
newValue: event.newValue,
oldValue: event.oldValue
})
})
}
}
7.2 性能分析
import { onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
let startTime
onMounted(() => {
startTime = performance.now()
})
onUnmounted(() => {
const endTime = performance.now()
console.log(`组件生命周期: ${endTime - startTime}ms`)
})
}
}
8. 最佳实践
8.1 代码组织
// composables/useCounter.js
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
export function useCounter(initialValue = 0) {
const count = ref(initialValue)
const double = computed(() => count.value * 2)
function increment() {
count.value++
}
function decrement() {
count.value--
}
return {
count,
double,
increment,
decrement
}
}
// components/Counter.vue
import { useCounter } from '../composables/useCounter'
export default {
setup() {
const { count, double, increment, decrement } = useCounter()
return {
count,
double,
increment,
decrement
}
}
}
8.2 状态管理
// store/counter.js
import { reactive } from 'vue'
export const store = reactive({
count: 0,
increment() {
this.count++
}
})
// components/Counter.vue
import { store } from '../store/counter'
export default {
setup() {
return {
store
}
}
}
9. 迁移建议
从 Vue2 迁移到 Vue3 时,建议采用渐进式迁移策略:
- 使用
@vue/composition-api插件在 Vue2 中提前使用组合式 API - 优先迁移新功能到组合式 API
- 使用
defineComponent包装组件获得更好的类型推导 - 注意生命周期钩子的变化
- 使用新的响应式 API 替代
Vue.observable
10. 总结
Vue3 带来了许多激动人心的新特性,特别是组合式 API 的引入,使得代码组织更加灵活,逻辑复用更加方便。通过合理使用这些特性,我们可以构建出更易维护、性能更好的应用。